|
The DVP Series proportional solenoid valves are precision-built 2-way control valves, utilizing a unique, patented valving principle. They offer an extremely high cycle life, fast response, linear flow gain, low hysteresis, low power consumption, and flows over 60 l/min. The valve provides air or gas flow control, and varies the output flow based on the current input to the solenoid.
|
 |
|
Features: |
|
• Industry standard for leak-free operation
• Over 1,000,000,000 cycles
• Extremely low hysteresis
• Fast response time
• Large flows in a small, sleek design
• Low heat rise/low power
• Robust stainless steel "spider" flat armature spring
• CE, RoHS compliant
• Proudly Made in USA
|
|
|
|
Valve Type: 2-Way, Proportional
Medium: Air & Compatible Gases (40 micron filter)
Pressure Range: Vac* to 100 psig
Max. Flow Tolerance: +10% / -0%
Power Consumption: 1.9 watts at 72˚F, 2.5 watts max.
Temperature Range: 32 to 120˚F
Voltage: 10 VDC (0.190 amps) or 20 VDC (0.095 amps)
Mounting: Manifold, #10-32 Male Stud
Seal Material: FKM standard; Nitrile, EPDM & Silicone available
Wetted Materials: Stainless Steel, PPS
Certifications: CE, RoHS, REACH
*Vacuum applications are reverse flow
|




|
|
|
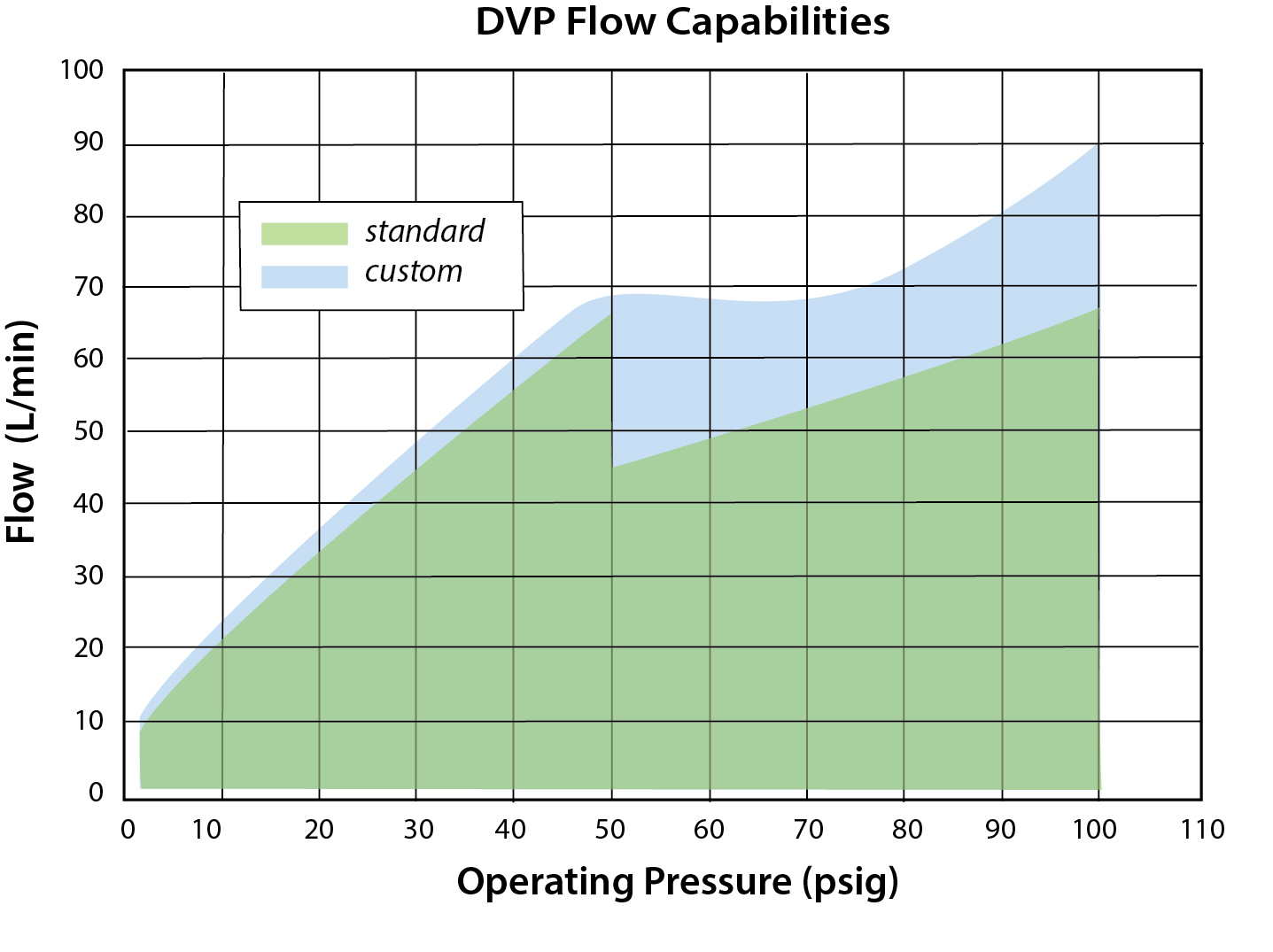
Clippard's newest DVP series proportional solenoid valves are precision-built 2-way control valves, utilizing Clippard's unique valving principle. This powerful series was designed as the next generation of Clippard's best-selling original EV line. With a lifespan of over a billion cycles; a solid, compact design; and extremely high flow rates, these valves are suitable for many applications across numerous industries.
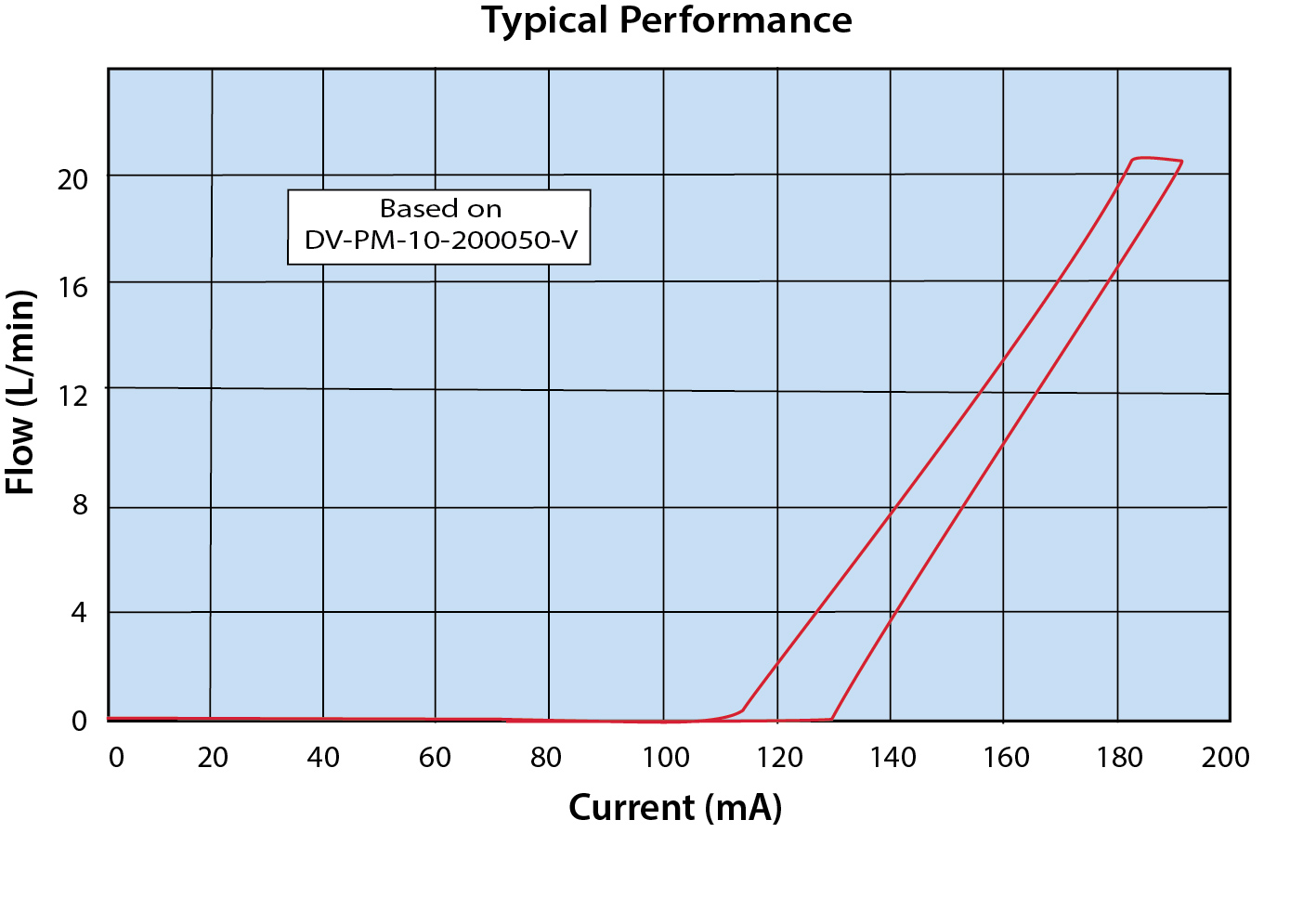
The DVP series provides air or gas flow control and varies the output flow based on the current input to the solenoid. The consistent gain (see chart) of this valve provides a high degree of control.
Controllability and overall value are the main features of the DVP series. The valve may be controlled using DC current, open or closed-loop control, and even PWM (pulse width modulation) to cover a large range of applications.








